Zambia Map Courtesy CIA World Factbook
The indigenous hunter-gatherer occupants of Zambia began to be displaced or absorbed by more advanced migrating tribes about 2,000 years ago. The major waves of Bantu-speaking immigrants—the Bantu expansion—began in the 15th century, with the greatest influx between the late 17th and early 19th centuries. They came primarily from the Luba and Lunda tribes of southern Democratic Republic of Congo and northern Angola but were joined in the 19th century by Ngoni peoples from the south. By the latter part of that century, the various peoples of Zambia were largely established in the areas they currently occupy. Except for the occasional Portuguese explorer, the area lay untouched by Europeans for centuries. After the mid-19th century, it was penetrated by Western explorers, missionaries, and traders. David Livingstone, in 1855, was the first European to see the magnificent waterfalls on the Zambezi River. He named them Victoria Falls after Queen Victoria, and the Zambian town near the falls is named after him. In 1888, Cecil Rhodes, spearheading British commercial and political interests in Central Africa, obtained a mineral rights concession from local chiefs. In the same year, Northern and Southern Rhodesia (now Zambia and Zimbabwe, respectively) were proclaimed a British sphere of influence. Southern Rhodesia was annexed formally and granted self-government in 1923, and the administration of Northern Rhodesia was transferred to the British Colonial Office in 1924 as a protectorate. Mining began in the Copperbelt in 1934. At independence, despite its considerable mineral wealth, Zambia faced major challenges. Domestically, there were few trained and educated Zambians capable of running the government, and the economy was largely dependent on foreign expertise. Abroad, three of its neighbors--Southern Rhodesia and the Portuguese colonies of Mozambique and Angola--remained under white-dominated rule. Rhodesia's white-ruled government unilaterally declared independence in 1965. In addition, Zambia shared a border with South African-controlled South-West Africa (now Namibia). Zambia's sympathies lay with forces opposing colonial or white-dominated rule, particularly in Southern Rhodesia. During the next decade, it actively supported movements such as the National Union for Total Independence of Angola (UNITA), the Zimbabwe African People's Union (ZAPU), the African National Congress of South Africa (ANC), and the South-West Africa People's Organization (SWAPO). Conflicts with Rhodesia resulted in the closing of Zambia's borders with that country and severe problems with international transport and power supply. However, the Kariba hydroelectric station on the Zambezi River provided sufficient capacity to satisfy the country's requirements for electricity. A railroad to the Tanzanian port of Dar es Salaam, built with Chinese assistance, reduced Zambian dependence on railroad lines south to South Africa and west through an increasingly troubled Angola. By the late 1970s, Mozambique and Angola had attained independence from Portugal. Zimbabwe achieved independence in accordance with the 1979 Lancaster House Agreement, but Zambia's problems were not solved. Civil war in the former Portuguese colonies generated an influx of refugees and caused continuing transportation problems. The Benguela Railroad, which extended west through Angola, was essentially closed to traffic from Zambia by the late 1970s. Zambia's strong support for the ANC, which had its external headquarters in Lusaka, created security problems as South Africa raided ANC targets in Zambia. In the mid-1970s, the price of copper, Zambia's principal export, suffered a severe decline worldwide. Zambia turned to foreign and international lenders for relief, but as copper prices remained depressed, it became increasingly difficult to service its growing debt. By the mid-1990s, despite limited debt relief, Zambia's per capita foreign debt remained among the highest in the world.
|
||||||||||||||||
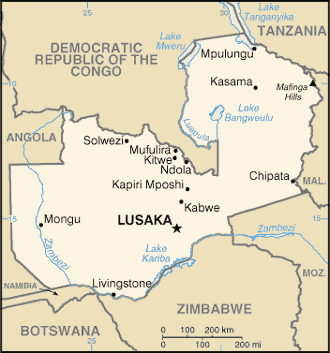 The Republic of Zambia is a landlocked country in south-central Africa. It borders the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Tanzania on the north-east, Malawi on the east, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana, and Namibia to the south, and Angola on the west. Formerly Northern Zambezia, and then, Northern Rhodesia, the country is named after the Zambezi river.
The Republic of Zambia is a landlocked country in south-central Africa. It borders the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Tanzania on the north-east, Malawi on the east, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana, and Namibia to the south, and Angola on the west. Formerly Northern Zambezia, and then, Northern Rhodesia, the country is named after the Zambezi river.