Botswana
Map Courtesy CIA World Factbook
The Batswana, a term also used to denote all citizens of Botswana, refers to the country's major ethnic group (the "Tswana" in South Africa), which came into the area from South Africa during the Zulu wars of the early 1800s. Prior to European contact, the Batswana lived as herders and farmers under tribal rule. In the 19th century, hostilities broke out between the Batswana and Boer settlers from the Transvaal. After appeals by the Batswana for assistance, the British Government on March 31, 1885 made "Bechuanaland" under a protectorate. The northern territory remained under direct administration and is today's Botswana, while the southern territory became part of the Cape Colony and is now part of the northwest province of South Africa; the majority of Setswana-speaking people today live in South Africa. Despite South African pressure, inhabitants of the Bechuanaland Protectorate, Basutoland (now Lesotho), and Swaziland in 1909 asked for and received British assurances that they would not be included in the proposed Union of South Africa. An expansion of British central authority and the evolution of tribal government resulted in the 1920 establishment of two advisory councils representing Africans and Europeans. Proclamations in 1934 regularized tribal rule and powers. A European-African advisory council was formed in 1951, and the 1961 constitution established a consultative legislative council. In June 1964, Britain accepted proposals for democratic self-government in Botswana. The seat of government was moved from Mafikeng, in South Africa, to newly established Gaborone in 1965. The 1965 constitution led to the first general elections and to independence in September 1966. Seretse Khama, a leader in the independence movement and the legitimate claimant to traditional rule of the Bamangwato, was elected as the first president, re-elected twice, and died in office in 1980. The presidency passed to the sitting vice president, Ketumile Masire, who was elected in his own right in 1984 and re-elected in 1989 and 1994. Masire retired from office in 1998. The presidency passed to the sitting vice president, Festus Mogae, who was elected in his own right in 1999. Mogae won a second term in elections held October 30, 2004. This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia article "Botswana". |
|||||||||
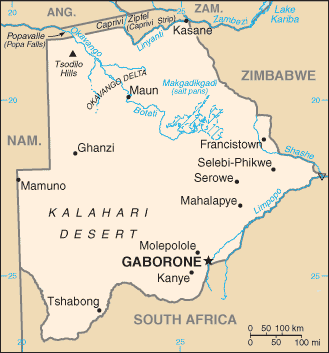 The Republic of Botswana (Lefatshe la Botswana) is a landlocked nation of southern Africa. Formerly the British protectorate of Bechuanaland, Botswana adopted its new name after becoming independent on September 30, 1966. It is bordered by South Africa to the south, Namibia to the west, Zambia to the north, and Zimbabwe to the northeast. The economy, closely tied to South Africa's, is dominated by cattle raising and mining, especially diamonds. The capital is Gaborone.
The Republic of Botswana (Lefatshe la Botswana) is a landlocked nation of southern Africa. Formerly the British protectorate of Bechuanaland, Botswana adopted its new name after becoming independent on September 30, 1966. It is bordered by South Africa to the south, Namibia to the west, Zambia to the north, and Zimbabwe to the northeast. The economy, closely tied to South Africa's, is dominated by cattle raising and mining, especially diamonds. The capital is Gaborone.