Niger Map Courtesy CIA World Factbook
During recent centuries, the nomadic Tuareg formed large confederations, pushed southward, and, siding with various Hausa states, clashed with the Fulani Empire of Sokoto, which had gained control of much of the Hausa territory in the late 18th century. In the 19th century, contact with the West began when the first European explorers—notably Mungo Park (British) and Heinrich Barth (German)—explored the area, searching for the source of the Niger River. Although French efforts at pacification began before 1900, dissident ethnic groups, especially the desert Tuareg, were not subdued until 1922, when Niger became a French colony. Niger's colonial history and development parallel that of other French West African territories. France administered its West African colonies through a governor general at Dakar, Senegal, and governors in the individual territories, including Niger. In addition to conferring French citizenship on the inhabitants of the territories, the 1946 French constitution provided for decentralization of power and limited participation in political life for local advisory assemblies. |
|||||||||
devastating drought and accusations of rampant corruption resulted in a military coup that overthrew the Diori regime. Col. Seyni Kountché and a small group of military ruled the country until Kountché's death in 1987. He was succeeded by his Chief of Staff, Col. Ali Saibou, who released political prisoners, liberalized some of Niger's laws and policies, and promulgated a new constitution. However, President Saibou's efforts to control political reforms failed in the face of union and student demands to institute a multi-party democratic system. The Saibou regime acquiesced to these demands by the end of 1990. New political parties and civic associations sprang up, and a national conference was convened in July 1991 to prepare the way for the adoption of a new constitution and the holding of free and fair elections. The debate was often contentious and accusatory, but under the leadership of Prof. André Salifou, the conference developed consensus on the modalities of a transition government. A transition government was installed in November 1991 to manage the affairs of state until the institutions of the Third Republic were put into place in April 1993. While the economy deteriorated over the course of the transition, certain accomplishments stand out, including the successful conduct of a constitutional referendum; the adoption of key legislation such as the electoral and rural codes; and the holding of several free, fair, and non-violent nationwide elections. Freedom of the press flourished with the appearance of several new independent newspapers.
In the culmination of an initiative started under the 1991 national conference, however, the government signed peace accords in April 1995 with all Tuareg and Toubou groups that had been in rebellion since 1990, claiming they lacked attention and resources from the central government. The government agreed to absorb some former rebels into the military and, with French assistance, help others return to a productive civilian life.
In April 1999, Baré was overthrown in a coup led by Maj. Daouda Malam Wanké, who established a transitional National Reconciliation Council to oversee the drafting of a constitution for a Fifth Republic with a French style semi-presidential system. In votes that international observers found to be generally free and fair, the Nigerien electorate approved the new constitution in July 1999 and held legislative and presidential elections in October and November 1999. Heading a coalition of the National Movement for a Developing Society (MNSD) and the Democratic and Social Convention (CDS), Mamadou Tandja won the presidency.
In July 2004, Niger held municipal elections nationwide as part of its decentralization process. Some 3,700 people were elected to new local governments in 265 newly established communes. The ruling MNSD party won more positions than any other political party; however, opposition parties made significant gains.
In November and December 2004, Niger held presidential and legislative elections. Tandja Mamadou was elected to his second 5-year presidential term with 65% of the vote in an election that international observers called generally free and fair. This was the first presidential election with a democratically elected incumbent and a test to Niger’s young democracy.
| This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia article "Niger". |
|
|
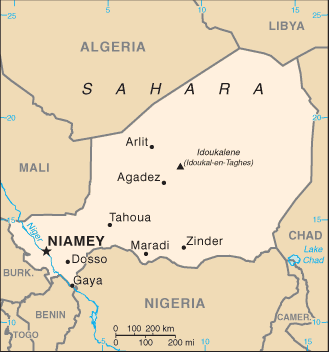 Niger is a landlocked sub-Saharan country in Western Africa situated north of Nigeria, east of Mali, and south of Algeria and Libya, named after the Niger river. The capital city is Niamey. Its proper English pronunciation is "nee-ZHAIR", although "NIGH-jer" is also acceptable. Its adjective form is Nigerien ("nee-ZHAIR-ee-an"), which should not be confused with Nigerian ("nigh-JEER-ee-an") for Nigeria. Considerable evidence indicates that about 600,000 years ago, humans inhabited what has since become the desolate Sahara of northern Niger. Niger was an important economic crossroads, and the empires of Songhai, Mali, Gao, Kanem, and Bornu, as well as a number of Hausa states, claimed control over portions of the area.
Niger is a landlocked sub-Saharan country in Western Africa situated north of Nigeria, east of Mali, and south of Algeria and Libya, named after the Niger river. The capital city is Niamey. Its proper English pronunciation is "nee-ZHAIR", although "NIGH-jer" is also acceptable. Its adjective form is Nigerien ("nee-ZHAIR-ee-an"), which should not be confused with Nigerian ("nigh-JEER-ee-an") for Nigeria. Considerable evidence indicates that about 600,000 years ago, humans inhabited what has since become the desolate Sahara of northern Niger. Niger was an important economic crossroads, and the empires of Songhai, Mali, Gao, Kanem, and Bornu, as well as a number of Hausa states, claimed control over portions of the area.