|
Nova Scotia
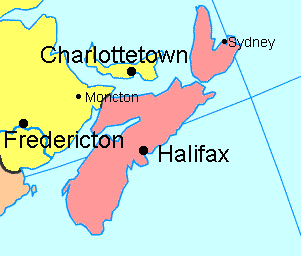
Nova Scotia (Latin for New Scotland; “Alba Nuadh” in Scottish Gaelic, la Nouvelle-Écosse in French) is a Canadian province on the North Atlantic coast. Nova Scotia has an area of 55,500 km² and a population of just under 940,000 (Nova Scotians). Its capital is Halifax. Paleo-Indians camped at locations in present-day Nova Scotia approximately 11,000 years ago. Archaic Indians are believed to have been present in the area between 1,000 and 5,000 years ago. Mi'kmaq, the First Nations of the province and region, are their direct descendants. The explorer John Cabot visited present-day Cape Breton in 1497. The first European settlement in Nova Scotia was established by French lead by Pierre Dugua, Sieur de Monts. They established the first capital for the colony Acadia at Port Royal in 1605 at the head of the Annapolis Basin. In 1620, the Plymouth Council for New England, under James I of England/James VI of Scotland designated the whole shorelines of Acadia and the Mid-Atlantic colonies south to the Chesapeake Bay as New England. In the latter 1620s, a group of Scots was sent by Charles I of England and Scotland to set up the colony of 'Nova Scotia'. (The Latin appellation was so stated in Sir William Alexander's 1621 land grant.) However owing to the signing of a peace treaty with France, the territory was given to the French and the Scots ordered to abandon their mission before their colony had been properly established. The French fortress at Louisbourg on Île Royale (Cape Breton Island) was established to guard the sea approaches to Quebec. This fortress was captured by American colonial forces, then returned by the British to France, then ceded again after the French and Indian War. British governing officials became increasingly concerned over the unwillingness of the Acadians, who were French-speaking, Catholic and the majority of colonists, to pledge allegiance to the British Crown. Despite a large number of mostly German foreign Protestants to be brought and settled along the South Shore in 1750, the colony remained mostly Acadian. In 1755, the British forcibly expelled the Acadians in what became known as the Great Expulsion. Most of these Acadians resettled in the French colony of Louisiana. The colony's jurisdiction changed during this time. In 1763 Cape Breton Island became part of Nova Scotia. In 1769, St. John's Island (now Prince Edward Island) became a separate colony. In 1784 the western, mainland portion of the colony was separated and became the province of New Brunswick. Cape Breton became a separate colony from 1784 to 1820, when it was rejoined. Ancestors of more than half of present-day Nova Scotians arrived in the period following the Acadian Expulsion. Approximately 30,000 United Empire Loyalists (American Tories) settled in Nova Scotia (when it comprised present-day Maritime Canada) following the defeat of the British in the American Revolutionary War. Approximately 3,000 of this group were slaves of African ancestry, about a third of which soon relocated themselves to Sierra Leone in 1792. Large numbers of Highland Scots emigrated to Cape Breton and the western portion of the mainland during the late 18th century and 19th century. An approximate thousand Ulster Scots settled in mainly central Nova Scotia during this time, as did just over a thousand farming migrants from Yorkshire and Northumberland between 1772 and 1775. Nova Scotia was the first colony in British North America and in the British Empire to achieve responsible government in January-February 1848 and become self-governing through the efforts of Joseph Howe. Nova Scotia was one of the four original provinces of Confederation, along with New Brunswick, Quebec, and Ontario. |
|||||||||||